Why You Shouldn’t Worry About Paying Capital Gains Tax When Selling Your Commercial Real Estate
The term “commercial property” can refer to both buildings that house businesses and land intended to generate revenue. In addition to commercial properties, there are some that house large housing developments. Commercial property can be anything from malls, warehouses, office buildings, and manufacturing facilities.

Source: The Caudle Group
Commercial property is traditionally considered a sound investment from the perspective of an investor. It may cost more to build and customize a building for a tenant, but the overall returns are greater.

Source: FA Commericial
In What Ways does the Sale of Commercial Property Affect Taxation?
Profits earned on the sale of assets such as stocks, bonds, or real estate are called capital gains. If the asset is sold for more than its original purchase price, it results in capital gain. It’s the difference between an asset’s sales price (higher) and the cost price (lower). Whenever the cost price is greater than the selling price, a capital loss results.
Profits arising from selling any commercial property you own and use for your business become taxable as short-term capital gains, despite how long you own the property.
Commercial property that is let out generates capital gains, regardless of whether the property is sold or not. The same shall apply to long-term holdings if the property is kept for more than 24 months, with a flat rate of 20% regardless of the value. For short-term capital gains derived from the sale of the property before 24 months, the tax will be imposed as normal income instead of short-term capital gains.
Advanced tax planning strategies are more critical now than ever because the Biden administration has proposed a 39.6% capital gains tax for wealthy individuals (Biden capital gain tax). In addition, investors in this category may see tax rates as high as 43.4% if capital gains tax and net investment tax are raised simultaneously. Shortly put, without planning, you could end up paying far more than you planned.
If you have an income in this range, advanced planning is imperative. To better understand the concept of Biden capital gain tax, here is a further explanation of the intricacies of this subject.
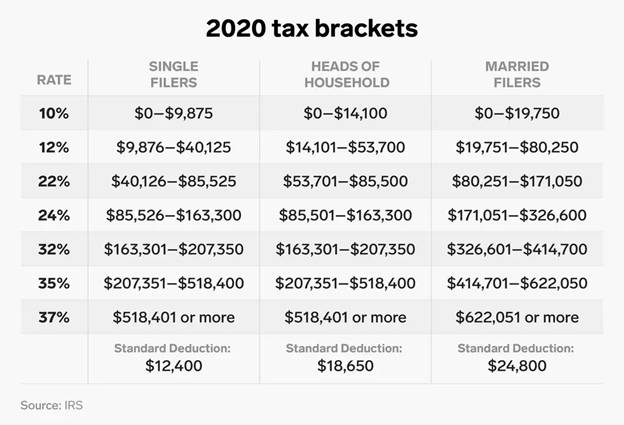
Source: Business Insider
Taxes for long-term and short-term capital gains are determined by your tax filing status and income category; capital gains are typically realized from selling an asset (for example, commercial real estate). The IRS Form 4797, Sale of Business Property, is typically used to file your income tax return.
The capital gains exclusions are not available to everyone. You are fully liable for taxes when:
- The seller doesn’t live in the home as his principal residence.
- You used a 1031 exchange to acquire the property within five years.
- It is the seller’s responsibility to pay expatriate taxes.
- For two of the past five years, the seller did not own or use the property as their primary residence (exceptions apply).
- Two years after the house sale, the seller sold another home and used the exclusion for capital gains on that sale.
Taking California as a case study, commercial real estate in California has been continually hit by the demand for more commercial real estate tax.
California has more than 40 million residents, so something must be working well with its great weather and beautiful beaches. But, unfortunately, it is extremely difficult to succeed financially in this state.
Living costs in California are among the highest in the United States, and it has high-income taxes as well. California’s tax system is just as expensive for investors as the federal system. As you pay more taxes, you will find it harder to build wealth.
If you’re asking, what is capital gains tax in California? Here is a detailed list:
California State Tax Rates and Tax Brackets
California Tax Brackets for Single Taxpayers
Taxable Income Rate
- $0 – $8,809 1.00%
- $8,809 – $20,883 2.00%
- $20,883 – $32,960 4.00%
- $32,960 – $45,753 6.00%
- $45,753 – $57,824 8.00%
- $57,824 – $295,373 9.30%
- $295,373 – $354,445 10.30%
- $354,445 – $590,742 11.30%
- $590,742 – $999,999 12.30%
- $1,000,000+ 13.30%
The following chart shows the tax brackets for married/registered domestic partners (RDP) who file joint returns in California (and widows who qualify).
Taxable Income Rate
- $0 – $17,618 1.00%
- $17,618 – $41,766 2.00%
- $41,766 – $65,920 4.00%
- $65,920 – $91,506 6.00%
- $91,506 – $115,648 8.00%
- $115,648 – $590,746 9.30%
- $590,746 – $708,890 10.30%
- $708,890 – $1,181,484 11.30%
- $1,181,484 – $1,999,999 12.30%
- $2,000,000+ 13.30%
Visit the Franchise Tax Board to find out the California Income Tax Rate for another filing status.
Section 1031 Tax-deferred Exchange
Many investors utilize Section 1031 like-kind exchanges as a way to defer capital gains until future years. Real estate investors use Section 1031 like-kind exchanges to replace a property they have disposed of with another of a similar kind. To complete a Section 1031 exchange properly, you must do much planning.
A 1031 exchange allows capital gains taxes to be deferred on a swap of one property for another in real estate. Realtors, title companies, and investors refer to the term based on the Internal Revenue Service’s (IRS’s) code Section 1031. Some people even insist on using it as a verb, as in: “Let’s 1031 this building for another.”
There is a lot to understand about IRS Section 1031 before using it as a real estate investor. For example, according to IRS rules, you can only exchange like-kind properties, and you can’t use them for vacation properties. Additionally, the tax implications and timeframe may be problematic. Here is what you need to know about 1031 if you’re contemplating it-or just curious.
1031 exchanges are swaps of one investment property for another (also known as like-kind exchanges or Starke exchanges). The majority of swaps are taxable as sales, but if yours meets the 1031 requirements, you won’t have to pay taxes at all or only need to pay limited taxes at the time of exchange.
Therefore, you are not required (in the IRS’s eyes) to cash out or recognize a capital gain if you change the form of your investment. Thus, your investments are tax-deferred. 1031s can be completed multiple times or frequently without limit. You can rollover one piece of real estate investment to another piece, another, and another.
Although you may profit on each swap, you don’t pay taxes on the sale until many years later. So in this scenario, you would pay only one tax, and that would be the long-term capital gains rate (currently between 15% and 20%, depending on your income-and 0% for some lower-income taxpayers).
“Like-kind” exchanges are the enigmatic normal phrase that means something quite different than what you may expect. You can exchange a ranch for raw land or an apartment building for a strip mall. It is surprising how liberal the rules are. There is even the possibility of exchanging businesses. It’s not all smooth sailing, however.
However, under which a former primary residence can be treated as investment property under the 1031 rules. Using 1031 for vacation home swaps is also possible, but this loophole has grown narrower in recent years.
Recently the Biden capital gain tax update has threatened to cancel the functionality of the 1031 exchange 2021 law. By this, it means real estate investors will find it harder to evade the high commercial real estate tax that comes with Biden capital gain tax.
With this setback, the question is, how can we then not worry about paying capital gains tax when selling commercial real estate? Worry no more.
There are ways to be free from the excessive burden of the commercial real estate tax, they are:
Deferred Sales Trusts or Delaware Statutory Trusts
If you are selling real estate or any other business assets, you are subject to capital gains tax; you can utilize a deferred sales trust to defer the tax. The proceeds of a sale are not collected at closing but are placed in trust and are only taxed when the funds are received from the sale. This strategy does not include capital gains tax deferral strategies that do not allow reinvestment of sale proceeds.
The Internal Revenue Code 453, also known as the deferred sales trust (Delaware statutory trusts), prevents taxpayers from paying taxes on money they haven’t received as part of an installment sale.
It is possible to sell a real estate asset to a deferred sales trust by selling it in installments. As a result, the trust can sell the real estate to the buyer without paying capital gains taxes on those gains.
Due to the actual sale price of the real property asset and the installment sales contract, the trust did not owe any capital gains taxes on the sale.
Furthermore, as the seller, you are not subject to capital gains taxes yet since you haven’t received the money from the sale in full (physically).
It is completely up to you how the installment contract from the sale is structured. Installment payments can begin right away or be deferred for several years.
Funds can be invested however you please by a third-party trustee. The principal from the sale of the property can be blended with interest income from the trust. Taxes on capital gains are only due when you begin receiving principal payments.
It takes a bit of work and special rules to set up a deferred sales trust and take advantage of its tax advantages.
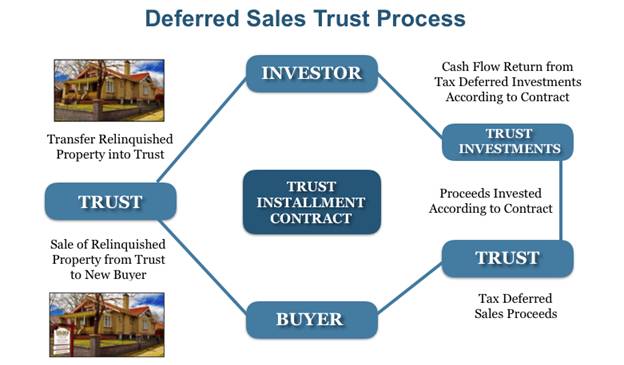
This is how you use a deferred sale trust (Delaware statutory trusts):
-
Third-party trusts are formed and are managed by third-party trustees.
-
A contract for installment sales is signed between the trust and the real estate owner.
-
Real estate is sold to the buyer, and the trust receives funds.
-
According to a seller’s instructions, the trustee invests or distributes installment payments.
-
Capital gains taxes are collected on the principal amount of installment payments a seller receives.
Source: Duplex Alerts
Whether you are selling an investment property, commercial property, or other business assets, you must pay capital gains taxes. If you use a deferred sales trust, you won’t avoid capital gains taxes, but you will have the option of deferring them while you reinvest the earnings.
How does the deferred sales trust benefit you?
The primary benefit of setting up a deferred sales trust is that you can defer capital gains while the sale proceeds can be invested to earn additional income. Investing more because of the capital gains taxes that haven’t been paid yet allows you to invest more.
Deferring taxes allows you to invest the full amount of your capital gain, for example, if you sold real estate for $1 million and deferred taxes. However, you’ll have to pay capital gains tax on the sale proceeds if you receive the proceeds yourself. Once taxes are paid, you have only $850,000 to invest.
For people who do not intend to invest in real estate anymore, a deferred sales trust can be an alternative to a 1031 exchange to defer their capital gains taxes. There are many investments that you can make with a deferred sales trust, including:
- Other real estate.
- Stocks.
- Angel investments.
- REITs.
- Bonds.
- Mutual funds.
- CDs.
In addition, deferred sales trusts permit you to receive payments as they become due. There are various ways to structure your principal payments, such as merely receiving income payments on the interest earned. If you sell a house, you can continue to receive cash flow from it. This is a great option for retirement income or as a cash flow generator.
A qualified intermediary may be able to put the funds into a deferred sales trust if you cannot complete the purchase of the replacement property for whatever reason. This prevents you from receiving money that you would have to pay taxes on.
A 1031 exchange entails selling your real estate and your replacement property to a qualified intermediary within 180 days. A qualified intermediary uses the proceeds of the sale of your property to purchase your replacement property.
It’s important to remember that if you can’t buy the new property within the timeframe allotted, your exchange will fail, and you’ll lose the opportunity to avoid capital gains taxes.
By transferring the money to a deferred sale trust, the qualified intermediary will give you more time to find and buy a replacement property. Reinvestment in a trust does not have a time limit, as is the case with 1031 exchanges.
Another way of deferring commercial real estate tax due to the threat of 1031 exchange rules, 2021 is by financing on properties where sellers agree to a down payment and finance the buyer’s purchase. This would allow sellers to defer taxes over a longer period and make income on the property (including interest).
Contact Us at Commercial Consult
If you’re interested in finding out more about how to sell your commercial real estate property, you can consult us at Commercial Consult.
We are a group of professionals with major expertise in commercial real estate and its transactions. We have a track record of top-notch services with massive clients’ reviews to show for it.
We believe with our partnership, we can help you maximize profit in every of your commercial real estate transactions. Contact us today!






 3100
Bristol
St., Suite 150,
3100
Bristol
St., Suite 150, info@commercialconsult.com
info@commercialconsult.com